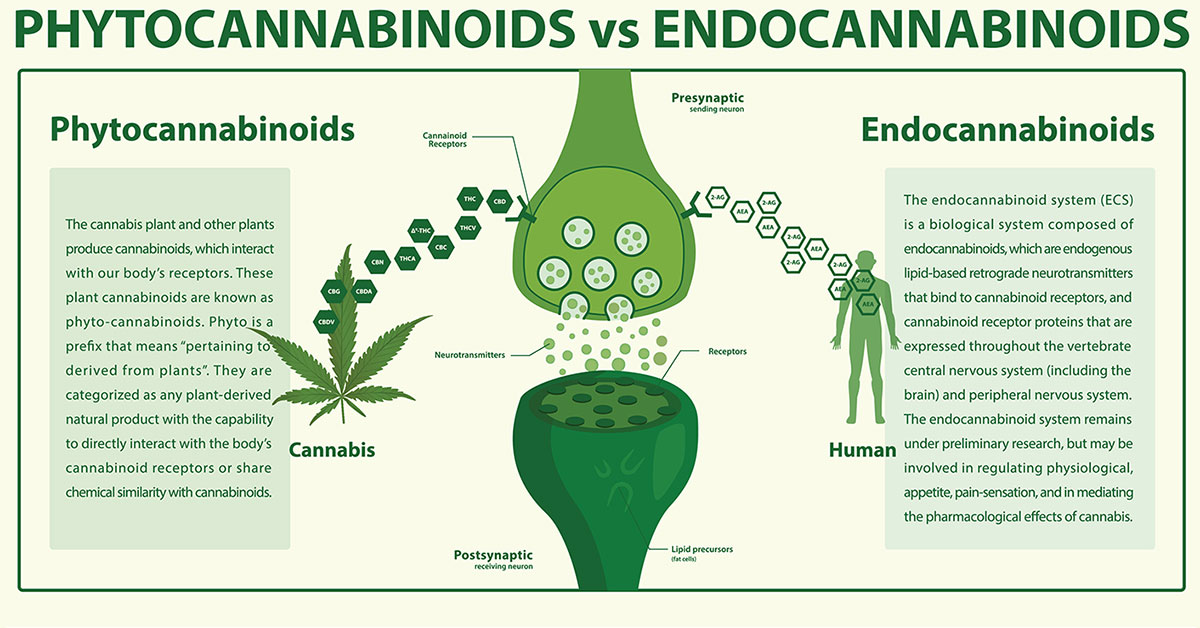
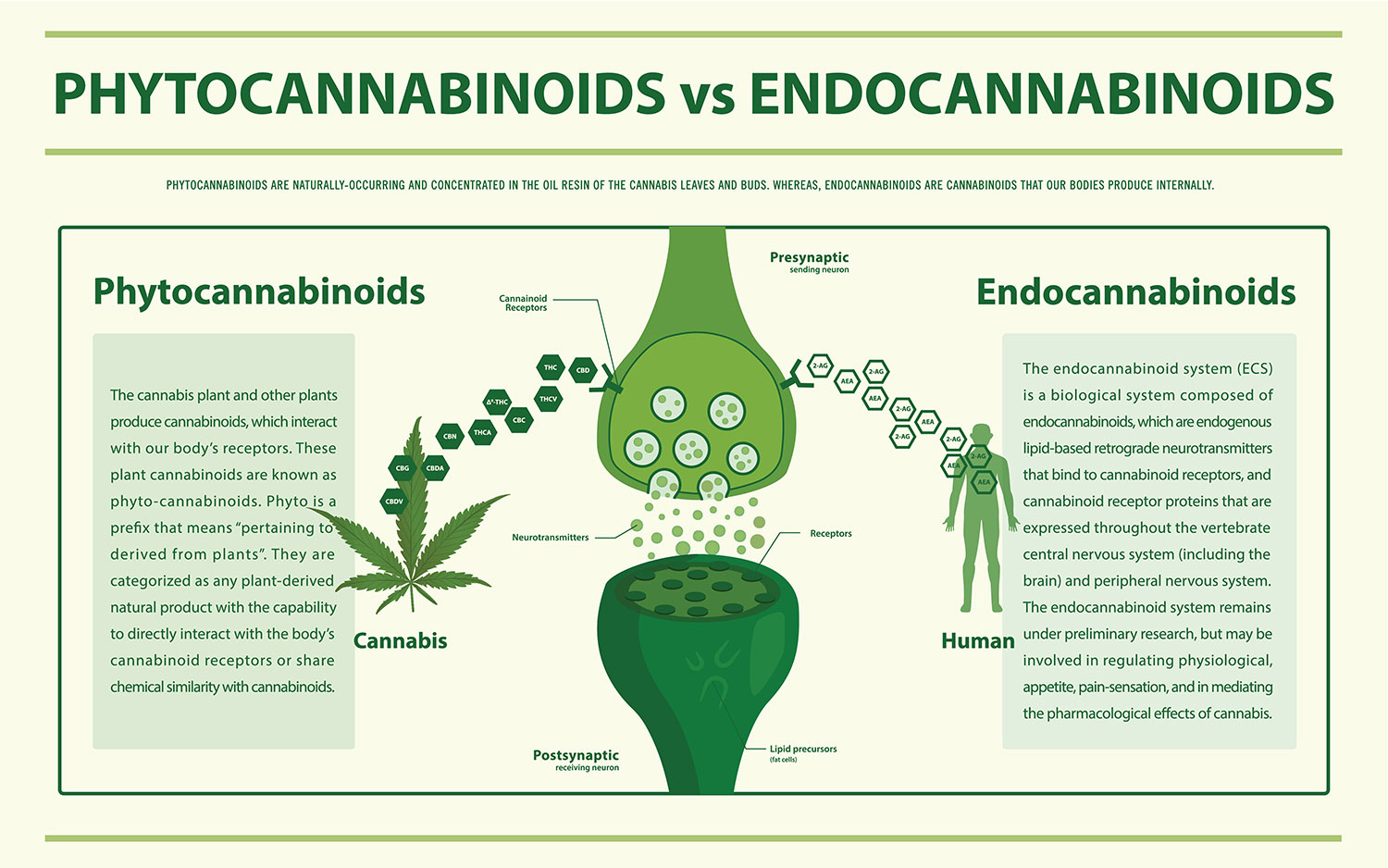
According to a study, exercise increases the cannabis-like substances of the body, which subsequently helps lessen inflammation and could potentially help in treating a number of conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.1✅ JOURNAL REFERENCE
DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1997559
Researchers discovered that exercise intervention in individuals with arthritis didn’t just lessen their pain, but also reduced inflammatory substances levels known as cytokines. It also increased cannabis-like substance levels known as endocannabinoids, which were made by their bodies. The way exercise led to these changes was by altering the gut microbes.
It’s already known that exercise reduces chronic inflammation, which subsequently leads to many diseases which includes heart disease, arthritis, and cancer, but not much is known as to the way it helps reduce inflammation.
A group of researchers evaluated 78 arthritis sufferers, with 38 of them performing 15 minutes of muscle-strengthening exercises each day for 6 weeks, and 40 of them not doing anything.
At the study’s conclusion, individuals who participated in the exercise intervention hadn’t only lessened their pain, but they also had more gut microbes of the anti-inflammatory substance producing kind, higher levels of endocannabinoids, and reduced cytokine levels.
The endocannabinoid increase was strongly associated with gut microbe changes and anti-inflammatory substances produced by gut microbes known as SCFAS. At least a third of the anti-inflammatory effects of the gut microbiome were because of the endocannabinoid increase.
The study demonstrates that the body’s cannabis-type substances are increased by exercise, which can have a positive effect on many health conditions.
With an increased interest in cannabidiol oil and other related supplements, it’s important to know that easy lifestyle interventions such as exercise can help modulate endocannabinoids.