Decaf, or decaffeinated coffee, is not a diuretic. Decaf coffee is just regular coffee with most of the caffeine removed, and the caffeine is the component in coffee that acts as a diuretic. Research has shown that caffeine levels need to be more than 500mg a day to have any significant diuretic effect. A diuretic induces the kidneys to excrete excess salts and water, thus producing more urine, which then results in urinating more frequently.
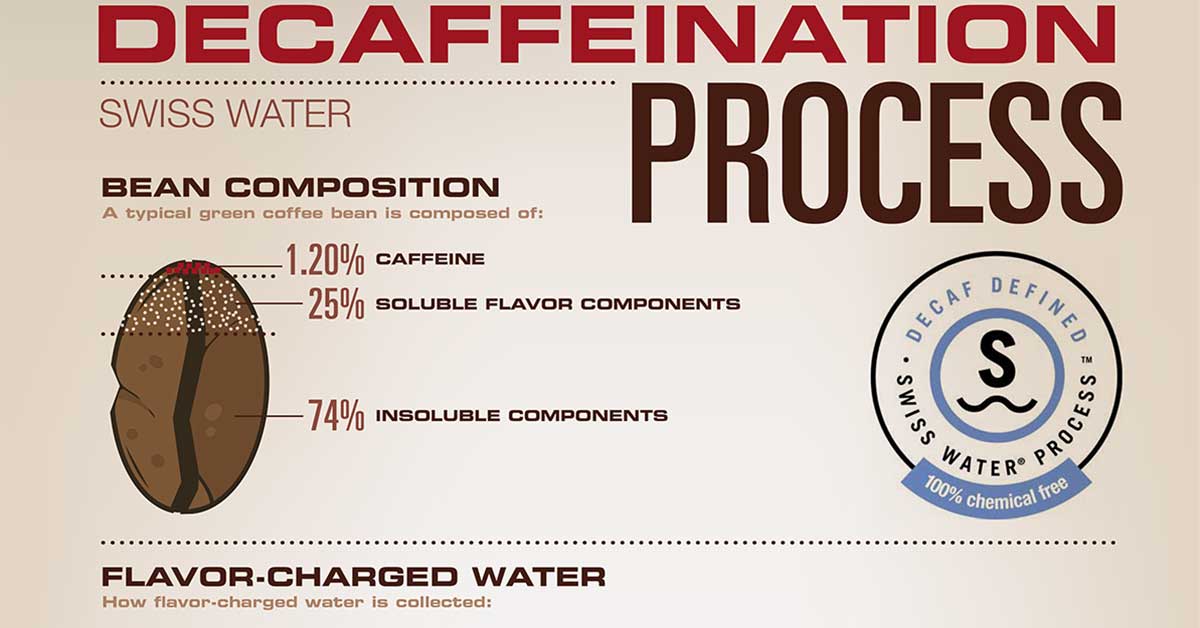
Decaf coffee is made from coffee beans which has had as much as 97% of the caffeine removed. There are several ways used for removing the caffeine from coffee beans. One method is by washing the beans in a solvent to extract the caffeine, then removing the solvent.
Decaf coffee isn’t completely free of caffeine; it can contain about 3 mg of caffeine per cup, with one study demonstrating a 6 ounce cup of decaffeinated coffee to contain 0 – 7 mg of caffeine, as opposed to a regular cup of coffee containing 70 – 140 mg of caffeine.
Because the beans are decaffeinated prior to roasting and grinding, the decaf coffee’s nutritional value is similar to regular coffee, although antioxidant levels can be as much as 15% less. The main antioxidant found in coffee is chlorogenic acid.
Some health benefits of decaf coffee:
Type 2 diabetes
Coffee consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, with each daily cup potentially reducing the risk up to 7%.
Liver function
Research has linked decaf coffee to a reduction in levels of liver enzymes, suggesting a protective effect.
Rectal cancer
Decaf coffee consumption of 2 or more cups daily has been associated with a lower risk of rectal cancer of as much as 48%.
Cognitive decline
Decaf coffee seems to have a positive effect on age-related cognitive decline, which could be due to the chlorogenic acid found in coffee.
Less heartburn
A common side effect of coffee for many people is acid reflux or heartburn. Decaf coffee consumption has been found to result in considerably less acid reflux in comparison to regular coffee consumption.
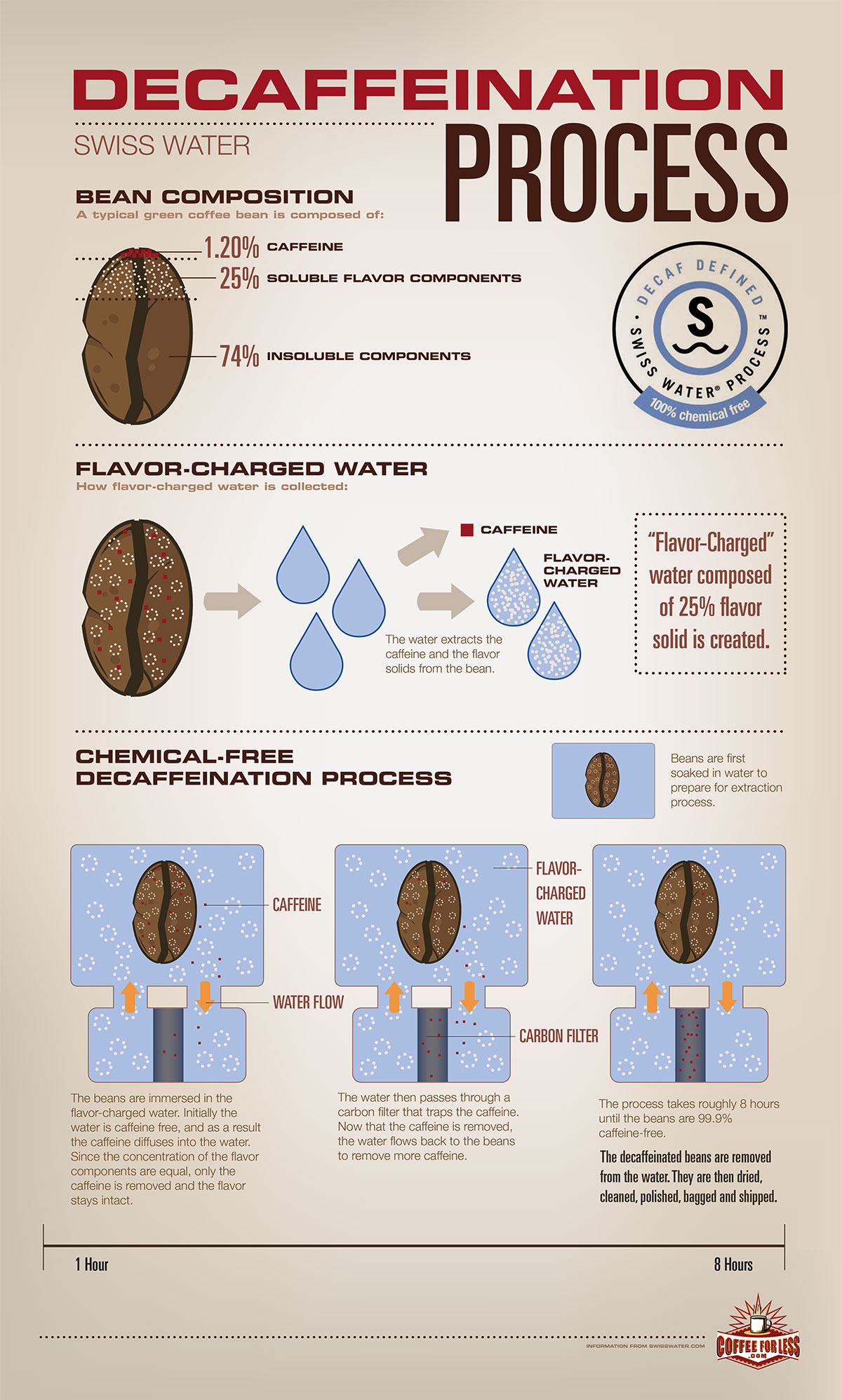
Image Source – coffeeforless