Researchers have conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies to determine the impact that certain foods have on LDL cholesterol levels. The meta-analysis included data from 37 guidelines, 20 randomized controlled trials, and 108 systematic reviews.1✅ JOURNAL REFERENCE
DOI: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.12.032
The study focused on individual foods rather than an overall dietary pattern, which is of more importance than any one food, and these study results are not intended to replace any existing dietary guidelines.
Guidelines and systematic reviews were examined before the researchers carried out their systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Only individuals not receiving lipid-lowering medication treatment were the target population of the studies. Only foods or nutrients associated with specific foods were included, and not dietary patterns, weight-loss diets, or supplements.
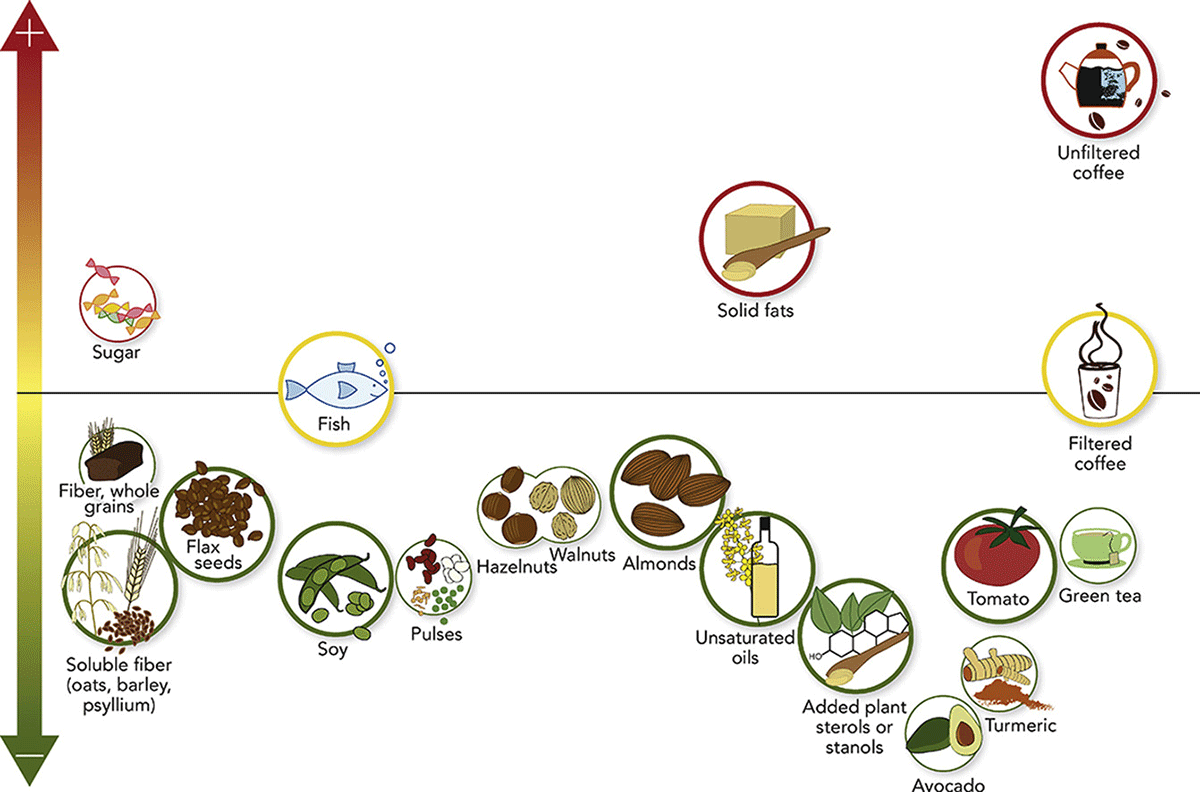
Various foods were examined and were graded according to the impact they had on LDL cholesterol levels. Certain foods had no effect, other foods contributed to small, moderate, or large LDL cholesterol level reductions, and some foods contributed to small, moderate, or large LDL cholesterol level increases.
Each food’s impact was judged according to its GRADE evidence, or Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation. a method used for grading the certainty or quality of scientific evidence. High or moderate GRADE levels provide researchers more confidence in the strength of their recommendations, in comparison to studies with low or very low results.
Certain beverages and foods with high or moderate GRADE levels had no impact on levels of LDL cholesterol, which include fish, filtered coffee, decaffeinated coffee as a substitute for regular coffee, fructose as a substitute for glucose, or sucrose.
High or moderate GRADE beverages and foods that support an LDL cholesterol level reduction include whole grains, green tea, turmeric, oils high in mono or poly-unsaturated fats like canola or olive oil, legumes like lentils and beans, almonds, hazelnuts and walnuts, foods with added plant stanols or sterols, avocados, tomatoes, soy protein, flaxseeds, foods high soluble fiber like barley, oats, and psyllium.
Low or very low GRADE level beverages and foods which support an LDL cholesterol level reduction include black tea, dark chocolate, berries, ginger, cumin, prebiotics and probiotics, and garlic.
Certain beverages and foods increased LDL cholesterol levels, which includes foods high in trans fatty acids, sugar and unfiltered coffee such as boiled coffee Scandinavian style.
Certain very low GRADE level foods had no clear effects, which included sweeteners, red meat, fruit juice, and dairy products, although current guidelines indicate that solid fats such as butter increase LDL cholesterol levels.